Terbium phosphide
Erbium compound
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names Terbium monophosphide, phosphanylidyneterbium | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | PTb |
| Molar mass | 189.899 |
| Appearance | Black crystals |
| Density | 6.82 g/cm3 |
| Structure | |
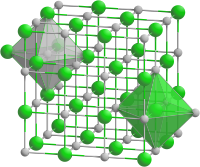
Crystal structure | Cubic |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions | Terbium nitride Terbium arsenide Terbium antimonide Terbium bismuthide |
Other cations | Gadolinium phosphide Dysprosium phosphide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Chemical compound
Terbium phosphide is an inorganic compound of terbium and phosphorus with the chemical formula TbP.[1][2]
Synthesis
TbP can be obtained by the reaction of terbium and red phosphorus at 800–1000 °C:
- 4 Tb + P4 → 4 TbP
The compound can also be obtained by the reaction of sodium phosphide and anhydrous terbium chloride at 700~800 °C.[3]
Physical properties
TbP undergoes a phase transition at 40 GPa from a NaCl-structure to a CsCl-structure.[4] The compound can be sintered with zinc sulfide to make a green phosphor layer.[5]
TbP forms crystals of a cubic system, space group Fm3m.[6]
Uses
The compound is a semiconductor used in high power, high frequency applications and in laser diodes and other photo diodes.[1]
References
- ^ a b "Terbium Phosphide". American Elements. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
- ^ Knorr, K.; Loidl, A.; Kjems, J. K.; Lüthi, B. (2 December 1979). "Magnetic excitations in TbP". Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials. 14 (2): 270–272. Bibcode:1979JMMM...14..270K. doi:10.1016/0304-8853(79)90136-7. ISSN 0304-8853. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
- ^ Rowley, Adrian T.; Parkin, Ivan P. (1 January 1993). "Convenient synthesis of lanthanide and mixed lanthanide phosphides by solid-state routes involving sodium phosphide". Journal of Materials Chemistry. 3 (7): 689–692. doi:10.1039/JM9930300689. ISSN 1364-5501. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
- ^ Adachi, Takafumi; Shirotani, Ichimin; Hayashi, Junichi; Shimomura, Osamu (28 December 1998). "Phase transitions of lanthanide monophosphides with NaCl-type structure at high pressures". Physics Letters A. 250 (4–6): 389–393. Bibcode:1998PhLA..250..389A. doi:10.1016/S0375-9601(98)00840-8. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
- ^ Raffius, G.; Kötzler, J. (7 February 1983). "Field-dependence of the first-order phase transition in terbium phosphide". Physics Letters A. 93 (8): 423–425. Bibcode:1983PhLA...93..423R. doi:10.1016/0375-9601(83)90477-2. ISSN 0375-9601. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
- ^ "Terbium Phosphide TbP". materialsproject.org. Retrieved 24 December 2021.










