| ZNF224 |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Human UniProt search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
2ELY, 2ELZ, 2EM0, 2EM6, 2EM7, 2EM8, 2EM9, 2EN1, 2EN8, 2ENA, 2ENC, 2EOQ, 2EOR, 2EQ4, 2YSP, 2YTH |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | ZNF224, BMZF-2, BMZF2, KOX22, ZNF255, ZNF27, ZNF233, zinc finger protein 224 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 194555; HomoloGene: 130663; GeneCards: ZNF224; OMA:ZNF224 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 19 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 19q13.31 | Start | 44,094,361 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 44,109,886 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - cerebellar hemisphere
- right hemisphere of cerebellum
- rectum
- gastric mucosa
- right uterine tube
- left ovary
- spleen
- left lobe of thyroid gland
- right ovary
- right lobe of thyroid gland
|
| | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 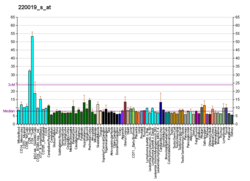 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - protein binding
- nucleic acid binding
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity
- metal ion binding
- DNA binding
- DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- sequence-specific DNA binding
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
| | Cellular component | - nucleus
- intracellular anatomical structure
- nuclear membrane
- transcription repressor complex
| | Biological process | - negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- transcription, DNA-templated
- negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | | |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 19: 44.09 – 44.11 Mb | n/a |
|---|
| PubMed search | [2] | n/a |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
|
















