Stearidonic acid
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
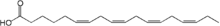
| Preferred IUPAC name (6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)-Octadeca-6,9,12,15-tetraenoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.127.224 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C18H28O2 |
| Molar mass | 276.420 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.9334 g/cm3 (15 °C) |
| Melting point | 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) decomposition |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  N verify (what is N verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) Infobox references | |
Stearidonic acid (SDA: C18H28O2; 18:4, n-3) is an ω-3 fatty acid, sometimes called moroctic acid.
Biosynthesis
It is biosynthesized from alpha-linolenic acid (ALA: C18H30O2; 18:3, n-3) by the enzyme delta-6-desaturase, which removes two hydrogen (H) atoms.
Stearidonic acid is a precursor to eicosapentaenoic acid.[1]
As it is a precursor to other fatty acids, there has been efforts to enhance the content off stearidonic acid in various crops, such as soybeans.[2]
SDA is also a precursor to N-acylethanolamine (NAEs).[3][4] Natural sources of this fatty acid are the seed oils of hemp, blackcurrant, corn gromwell,[5] and Echium plantagineum, and the cyanobacterium Spirulina. SDA can also be synthesized in a lab. A GMO soybean source is approved by the European Food Safety Authority.[6]
See also
References
- ^ Calder, Philip C. (2012). "Mechanisms of Action of (N-3) Fatty Acids". The Journal of Nutrition. 142 (3): 592S–599S. doi:10.3945/jn.111.155259. PMID 22279140.
- ^ Garg, Monika; Sharma, Natasha; Sharma, Saloni; Kapoor, Payal; Kumar, Aman; Chunduri, Venkatesh; Arora, Priya (2018). "Biofortified Crops Generated by Breeding, Agronomy, and Transgenic Approaches Are Improving Lives of Millions of People around the World". Frontiers in Nutrition. 5. doi:10.3389/fnut.2018.00012. PMC 5817065. PMID 29492405.
- ^ Galasso, Incoronata; Russo, Roberto; Mapelli, Sergio; Ponzoni, Elena; Brambilla, Ida M.; Battelli, Giovanna; Reggiani, Remo (2016-05-20). "Variability in Seed Traits in a Collection of Cannabis sativa L. Genotypes". Frontiers in Plant Science. 7: 688. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.00688. ISSN 1664-462X. PMC 4873519. PMID 27242881.
- ^ PubChem. "Stearidonic acid". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2022-11-22.
- ^ "Corn Gromwell". NIAB. Archived from the original on 2011-07-04.
- ^ "Scientific Opinion on genetically modified soybean MON 87769". European Food Safety Authority. 2014-05-16. Retrieved 2019-02-18.
- v
- t
- e
- Propionic (C3)
- Butyric (C4)
- Valeric (C5)
- Caproic (C6)
- Enanthic (C7)
- Caprylic (C8)
- Pelargonic (C9)
- Capric (C10)
- Undecylic (C11)
- Lauric (C12)
- Tridecylic (C13)
- Myristic (C14)
- Pentadecylic (C15)
- Palmitic (C16)
- Margaric (C17)
- Stearic (C18)
- Nonadecylic (C19)
- Arachidic (C20)
- Heneicosylic (C21)
- Behenic (C22)
- Tricosylic (C23)
- Lignoceric (C24)
- Pentacosylic (C25)
- Cerotic (C26)
- Carboceric (C27)
- Montanic (C28)
- Nonacosylic (C29)
- Melissic (C30)
- Hentriacontylic (C31)
- Lacceroic (C32)
- Psyllic (C33)
- Geddic (C34)
- Ceroplastic (C35)
- Hexatriacontylic (C36)
- Heptatriacontanoic (C37)
- Octatriacontanoic (C38)
- Nonatriacontanoic (C39)
- Tetracontanoic (C40)
- Octenoic (8:1)
- Decenoic (10:1)
- Decadienoic (10:2)
- Lauroleic (12:1)
- Laurolinoleic (12:2)
- Myristovaccenic (14:1)
- Myristolinoleic (14:2)
- Myristolinolenic (14:3)
- Palmitolinolenic (16:3)
- Palmitidonic (16:4)
- α-Linolenic (18:3)
- Stearidonic (18:4)
- α-Parinaric (18:4)
- Dihomo-α-linolenic (20:3)
- Eicosatetraenoic (20:4)
- Eicosapentaenoic (20:5)
- Clupanodonic (22:5)
- Docosahexaenoic (22:6)
- 9,12,15,18,21-Tetracosapentaenoic (24:5)
- 6,9,12,15,18,21-Tetracosahexaenoic (24:6)
- Myristoleic (14:1)
- Palmitovaccenic (16:1)
- α-Eleostearic (18:3)
- β-Eleostearic (trans-18:3)
- Punicic (18:3)
- 7,10,13-Octadecatrienoic (18:3)
- 9,12,15-Eicosatrienoic (20:3)
- β-Eicosatetraenoic (20:4)
- 8-Tetradecenoic (14:1)
- 12-Octadecenoic (18:1)
- Linoleic (18:2)
- Linolelaidic (trans-18:2)
- γ-Linolenic (18:3)
- Calendic (18:3)
- Pinolenic (18:3)
- Dihomo-linoleic (20:2)
- Dihomo-γ-linolenic (20:3)
- Sciadonic (20:3)
- Arachidonic (20:4)
- Adrenic (22:4)
- Osbond (22:5)
- Palmitoleic (16:1)
- Vaccenic (18:1)
- Rumenic (18:2)
- Paullinic (20:1)
- 7,10,13-Eicosatrienoic (20:3)
- Sapienic (16:1)
- Gadoleic (20:1)
- 4-Hexadecenoic (16:1)
- Petroselinic (18:1)
- 8-Eicosenoic (20:1)
 | This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e












