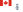Mark 32 Surface Vessel Torpedo Tubes
| Mark 32 torpedo tubes | |
|---|---|
 Mark 32 torpedo tubes mounted on ROCS Tzu I | |
| Type | Torpedo tube |
| Place of origin | United States |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1960–present |
| Used by | United States Navy |
| Wars | Cold War |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Ordnance Technology Service[1] |
| Variants | Mod 5 Mod 7 Mod 9 Mod 11 Mod 14 Mod 15 Mod 17 Mod 19 |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 2,230 lb (1,010 kg) |
Launch platform | Surface vessel |
Mark 32 Surface Vessel Torpedo Tubes (Mk 32 SVTT) is a torpedo launching system designed for the United States Navy.[2]
History
The Mark 32 has been the standard anti-submarine torpedo launching system aboard United States Navy surface vessels since its introduction[3] in 1960,[citation needed] and is in use aboard the warships of several other navies.[3]
During the FRAM Program, Fletcher, Allen M. Sumner and Gearing-class destroyers were modernized and fitted with two Mark 32 torpedo tubes on each side of their midship. The torpedo tubes' service extended to multiple other countries such as Mexico, South Korea, Taiwan, Turkey, Egypt and many more due to the fact that decommissioned American ships were bought or transferred over to them throughout the years, notably Oliver Hazard Perry-class frigates.
Japan uses the HOS-301 torpedo tubes which are redesignated version of the Mark 32.
Design
Most versions (referred to as modifications or mods) are triple-tube sets that can be rotated or trained to face a target.[3] The exception is the Mod 9 sets, which only have two tubes and are fixed in position.[3] The Mark 32 can fire 12.75-inch (324 mm) torpedoes of the Mark 44, Mark 46, Mark 50 (from the Mod 17 tubes onwards),[3][4] and Mark 54[citation needed] designs, and can be modified to use other torpedoes (such as the MU90 Impact aboard Royal Australian Navy frigates, or Royal Navy units using Sting Ray torpedoes).[5][6] The tubes are designed to be fired remotely, but manual firing controls are fitted as a backup to all but the Spruance-class destroyer's Mod 15 sets, as all aspects of the tubes' operation are controlled remotely.[3] The launch is powered by compressed air[3] in a rear flask, which doubles as each tube's breech, and the torpedoes are fire-and-forget weapons.[citation needed]
The launcher can be made from fibreglass, or with a fibreglass liner encased in metal.[3] The tubes were designed to be weatherproof and capable of storing torpedoes for long periods, but this is only practical with regular maintenance.[citation needed] Each triple-tube set weighs around 2,230 pounds (1,010 kg) unloaded, with variations between mods.[3]
On board ships
 United States
United States
- Fletcher-class destroyer
- Allen M. Sumner-class destroyer
- Gearing-class destroyer
- Mitscher-class destroyer
- Forrest Sherman-class destroyer
- Farragut-class destroyer
- Charles F. Adams-class destroyer
- Spruance-class destroyer
- Kidd-class destroyer
- Arleigh Burke-class destroyer
- Claud Jones-class destroyer escort
- Knox-class frigate
- Oliver Hazard Perry-class frigate

- Long Beach-class cruiser
- Leahy-class cruiser
- Bainbridge-class cruiser
- Belknap-class cruiser
- Truxtun-class cruiser
- California-class cruiser
- Virginia-class cruiser
- Ticonderoga-class cruiser
- Hamilton-class cutter
- Treasury-class cutter
 Japan
Japan
- Tachikaze-class destroyer
- Hatakaze-class destroyer
- Ayanami-class destroyer
- Akizuki-class destroyer (1959)

- Yamagumo-class destroyer
- Takatsuki-class destroyer
- Minegumo-class destroyer
- Hatsuyuki-class destroyer
- Asagiri-class destroyer
- Murasame-class destroyer
- Takanami-class destroyer
- Kongō-class destroyer
- Atago-class destroyer
- Maya-class destroyer
- Akizuki-class destroyer (2010)
- Asahi-class destroyer
- Isuzu-class destroyer escort
- Chikugo-class destroyer escort
- Ishikari-class destroyer escort
- Yūbari-class destroyer escort
- Abukuma-class destroyer escort
- Kashima-class training ship
- Asuka-class experimental ship
 Canada
Canada
- St. Laurent-class destroyer
- Restigouche-class destroyer
- Mackenzie-class destroyer
- Annapolis-class destroyer
- Iroquois-class destroyer
- Halifax-class frigate
 Taiwan
Taiwan
- Kee Lung-class destroyer

- Chi Yang-class frigate
- Cheng Kung-class frigate
 Italy
Italy
- Audace-class destroyer
- Durand de la Penne-class destroyer
- Centauro-class frigate
- Bergamini-class frigate

- Alpino-class frigate
- Lupo-class frigate
- Maestrale-class frigate
- Albatros-class corvette
 Australia
Australia
- Perth-class destroyer
- Hobart-class destroyer
- Anzac-class frigate
 South Korea
South Korea
- Ulsan-class frigate
- Donghae-class corvette
- Pohang-class corvette
- Gwanggaeto the Great-class destroyer
- Chungmugong Yi Sun-sin-class destroyer
- Sejong the Great-class destroyer
- Incheon-class frigate
- Daegu-class frigate
 Indonesia
Indonesia
- Claud Jones-class destroyer escort
- Ahmad Yani-class frigate
- Fatahillah-class corvette
See also
References

- ^ "MK32". Ordnance Technology Service, Inc. Retrieved 2021-09-04.
- ^ "Jane's: SVTT Mk 32 (United States), Weapon handling and launching systems". Archived from the original on 2010-06-11. Retrieved 2010-03-04.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Friedman, Norman (2006). The Naval Institute Guide to World Naval Weapon Systems (5th ed.). Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press. pp. 754–5.
- ^ "Post-WWII US torpedoes at www.NavWeaps.com". Archived from the original on 2019-03-27. Retrieved 2019-01-27.
- ^ Fish, Tim; Grevatt, Jon (24 June 2008). "Australia's HMAS Toowoomba test fires MU90 torpedo". Jane's Navy International. Jane's Information Group.
- ^ Chant, Chris (2005). Submarine Warfare Today: The World's Deadliest Underwater Systems. Leicester: Silverdale Books. p. 143. ISBN 1-84509-158-2.
- v
- t
- e