Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
| ATP5IF1 |
|---|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | ATP5IF1, ATPI, ATPIP, IP, ATPase inhibitory factor 1, ATP synthase inhibitory factor subunit 1, ATPIF1 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 614981; MGI: 1196457; HomoloGene: 40581; GeneCards: ATP5IF1; OMA:ATP5IF1 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 1 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 1p35.3 | Start | 28,236,109 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 28,246,906 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 4 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 4|4 D2.3 | Start | 132,257,866 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 132,260,970 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - left testis
- apex of heart
- right testis
- Brodmann area 9
- prefrontal cortex
- mucosa of transverse colon
- superior frontal gyrus
- primary visual cortex
- olfactory zone of nasal mucosa
- right auricle
|
| | Top expressed in | - Paneth cell
- epithelium of small intestine
- atrium
- Ileal epithelium
- external carotid artery
- migratory enteric neural crest cell
- proximal tubule
- right kidney
- internal carotid artery
- medial vestibular nucleus
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS |  | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - 5-formyltetrahydrofolate cyclo-ligase activity
- enzyme inhibitor activity
- protein homodimerization activity
- ATPase binding
- calmodulin binding
- ATPase inhibitor activity
- angiostatin binding
- enzyme binding
- mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex binding
| | Cellular component | - mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex
- cell surface
- mitochondrion
| | Biological process | - regulation of ATP metabolic process
- positive regulation of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling pathway
- negative regulation of ATP-dependent activity
- tetrahydrofolate interconversion
- positive regulation of proteolysis involved in cellular protein catabolic process
- negative regulation of hydrolase activity
- generation of precursor metabolites and energy
- reactive oxygen species metabolic process
- negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation
- heme biosynthetic process
- regulation of protein targeting to mitochondrion
- angiogenesis
- erythrocyte differentiation
- mitochondrial depolarization
- protein homooligomerization
- protein homotetramerization
- folic acid-containing compound biosynthetic process
- positive regulation of autophagy of mitochondrion in response to mitochondrial depolarization
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | |
|---|
ENSG00000130770
ENSG00000285390 |
| |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_178191
NM_016311
NM_178190 |
| |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | |
|---|
NP_057395
NP_835497
NP_835498 |
| |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 1: 28.24 – 28.25 Mb | Chr 4: 132.26 – 132.26 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
ATPase inhibitor, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATPIF1 gene.[5][6]
This gene encodes a mitochondrial ATPase inhibitor. Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and three transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified.[6]
It prevents ATPase from switching to ATP hydrolysis during collapse of the electrochemical gradient, for example during oxygen deprivation [7] ATP synthase inhibitor forms a one-to-one complex with the F1 ATPase, possibly by binding at the alpha-beta interface. It is thought to inhibit ATP synthesis by preventing the release of ATP.[8] The inhibitor has two oligomeric states, dimer (the active state) and tetramer. At low pH, the inhibitor forms a dimer via antiparallel coiled coil interactions between the C-terminal regions of two monomers. At high pH, the inhibitor forms tetramers and higher oligomers by coiled coil interactions involving the N terminus and inhibitory region, thus preventing the inhibitory activity.[7]
| Mitochondrial ATPase inhibitor, IATP |
|---|
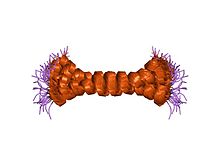 c-terminal coiled-coil domain from bovine if1 |
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Symbol | IATP |
|---|
| Pfam | PF04568 |
|---|
| InterPro | IPR007648 |
|---|
| SCOP2 | 1hf9 / SCOPe / SUPFAM |
|---|
| Available protein structures: |
|---|
| Pfam | structures / ECOD |
|---|
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
|---|
| PDBsum | structure summary |
|---|
|
References
- ^ a b c ENSG00000285390 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000130770, ENSG00000285390 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000054428 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Ichikawa N, Ushida S, Kawabata M, Masazumi Y (Mar 2000). "Nucleotide sequence of cDNA coding the mitochondrial precursor protein of the ATPase inhibitor from humans". Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 63 (12): 2225–2227. doi:10.1271/bbb.63.2225. PMID 10664857.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: ATPIF1 ATPase inhibitory factor 1".
- ^ a b Cabezon E, Butler PJ, Runswick MJ, Carbajo RJ, Walker JE (November 2002). "Homologous and heterologous inhibitory effects of ATPase inhibitor proteins on F-ATPases". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (44): 41334–41. doi:10.1074/jbc.M207169200. PMID 12186878. S2CID 25160113.
- ^ van Raaij MJ, Orriss GL, Montgomery MG, Runswick MJ, Fearnley IM, Skehel JM, et al. (December 1996). "The ATPase inhibitor protein from bovine heart mitochondria: the minimal inhibitory sequence". Biochemistry. 35 (49): 15618–25. doi:10.1021/bi960628f. PMID 8961923.
External links
Further reading
- Cabezón E, Runswick MJ, Leslie AG, Walker JE (2002). "The structure of bovine IF(1), the regulatory subunit of mitochondrial F-ATPase". EMBO J. 20 (24): 6990–6996. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.24.6990. PMC 125800. PMID 11742976.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, Derge JG, Klausner RD, Collins FS, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–16903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, Otsuki T, Sugiyama T, Irie R, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–45. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, Shenmen CM, Grouse LH, Schuler G, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–2127. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Burwick NR, Wahl ML, Fang J, Zhong Z, Moser TL, Li B, et al. (2005). "An Inhibitor of the F1 subunit of ATP synthase (IF1) modulates the activity of angiostatin on the endothelial cell surface". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (3): 1740–1745. doi:10.1074/jbc.M405947200. PMC 1201548. PMID 15528193.
- Andersen JS, Lam YW, Leung AK, Ong SE, Lyon CE, Lamond AI, et al. (2005). "Nucleolar proteome dynamics". Nature. 433 (7021): 77–83. Bibcode:2005Natur.433...77A. doi:10.1038/nature03207. PMID 15635413. S2CID 4344740.
- Cortés-Hernández P, Domínguez-Ramírez L, Estrada-Bernal A, Montes-Sánchez DG, Zentella-Dehesa A, De Gómez-Puyou MT, et al. (2005). "The inhibitor protein of the F1F0-ATP synthase is associated to the external surface of endothelial cells". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 330 (3): 844–849. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.03.064. PMID 15809073.
- Lim J, Hao T, Shaw C, Patel AJ, Szabó G, Rual JF, et al. (2006). "A protein-protein interaction network for human inherited ataxias and disorders of Purkinje cell degeneration". Cell. 125 (4): 801–814. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.032. PMID 16713569. S2CID 13709685.
- Ma J, Dempsey AA, Stamatiou D, Marshall K, Liew C (2007). "Identifying leukocyte gene expression patterns associated with plasma lipid levels in human subjects". Atherosclerosis. 191 (1): 63–72. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.05.032. PMID 16806233.
- Contessi S, Comelli M, Cmet S, Lippe G, Mavelli I (2008). "IF(1) distribution in HepG2 cells in relation to ecto-F(0)F (1)ATPsynthase and calmodulin". J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 39 (4): 291–300. doi:10.1007/s10863-007-9091-0. PMID 17851741. S2CID 85086145.
This article incorporates text from the public domain
Pfam and
InterPro: IPR007648


















